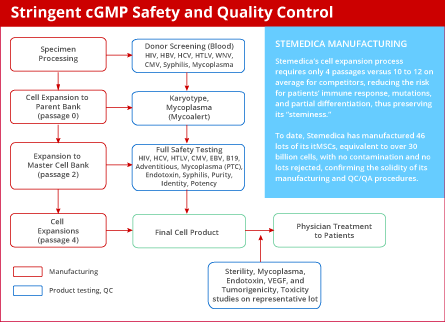
Stemedica carefully screens each specimen in both the manufacturing process and the quality-control phases. To date, Stemedica has manufactured the equivalent of 100 billion cells, and there has been no report of contamination or rejected lots.
Stemedica allogeneic stem cells have the following competitive advantages:
- Reproducibility: Stemedica can currently produce more than 450,000 doses of itMSCs from an individual donor and 180,000 doses of itNSCs from a different donor, while maintaining strict manufacturing control over cell quality and performance. These numbers will increase dramatically with new manufacturing processes being put in pace.
- Immune Privilege: Autologous cells (derived from the same organism) were considered more immune privileged than allogeneic cells (not from same organism) thus not causing immune responses. The main cause of rejection and clearance of allogeneic stem cells from the host is expression of HLA-DR receptor on the surface, which leads to immune responses from the host organism. Stemedica is growing itMSCs and itNSCs under low-oxygen conditions; this reduces the presence of HLA-DR to less than 2 percent, therefore reducing the chance of immune response.
- Cost: Autologous stem cell therapy is more expensive than allogeneic therapy in the long run. Allogeneic cells are available off-the-shelf and already tested, but autologous cells must be retrieved from the patient by injections or invasive surgical procedure, tested, expanded individually and, finally, re-introduced into the patient. Each treatment is cheaper, but after several treatments, costs could get higher then the more effective allogeneic treatment.
- Scalability: Stemedica’s itMSCs and itNSCs are highly scalable with hundreds of thousands to millions of treatment doses deriving from a healthy donor sample. Autologous cells are not scalable because they need to be retrieved surgically from each individual patient.

